Melatonin is one of the most important neurotransmitters released in the brain. In the last article we explored how melatonin directs the circadian rhythm of the body, and we’ve also seen the importance of breathing for better sleep and brain health. Before that we saw how brain waves direct both REM sleep cycles. Now we’re going to dive deeper.
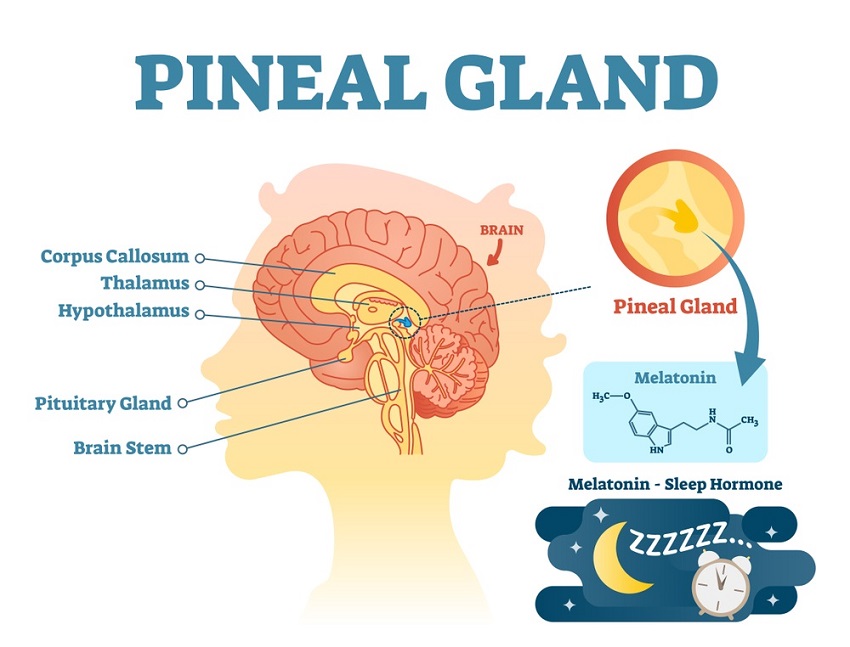
Until recently, the function of the pineal gland was confined to release of melatonin for sleep. Today, neuroscientists are understanding that the pineal gland is the master endocrine hormone.
As with anything in life, there is always a close link to your teeth. At the end of the article I explore the link between fluoride and your pineal gland. In this article we’ll explore why the pineal gland is critical for a better brain.
The Pineal Gland as the Third Eye
The philosopher Rene Descartes called the pineal gland the “seat of the soul,” and is revered in many spiritual traditions as a source of intuition and inner vision. Many ancient cultures also discussed the pineal gland, also known as the third-eye, as a centrepiece of the brain. Evolutionary evidence shows that the pineal gland was once an actual third eye with a physical lens in some creatures. In humans today, it acts as a connection between the two eyes to receive light.
It detects light and controls the circadian rhythm of the body. In darkness it releases melatonin, which acts as the body’s internal signal for night time. These signals cool and slow the body to prepare for sleep.
What is Melatonin? 15 Functions, Uses and Potential Benefits
Beyond the circadian sleep cycle, the pineal gland acts as the master endocrine gland. However, the benefits of melatonin are now realized all over the body. Melatonin has many roles all over the body, including:
1) Treating Depression
Disrupted sleep cycles can increase risk of depression. Studies show melatonin could possibly help reduce symptoms of seasonal depression by helping with the sleep cycle.
2) Reversing Anxiety
Sleep deprivation can associate with anxiety-like behaviour. Research has shown that melatonin treatment may prevent these symptoms.
3) Digestive Health, Stomach Ulcers and Heart Burn
Overall, melatonin is an anti-oxidant for the gut and digestive system. Melatonin and L-tryptophan have been shown to be protective to the digestive system and studies have demonstrated that melatonin may help heal stomach ulcers associated with aspirin.
Melatonin may also help increase gastrin levels, which has an anti-inflammatory action on the digestive system.
4) Anti-Cancer and Tumor Treatment
The immune system is known to influence stress hormones. Low melatonin levels are found in women with breast cancer and men with prostate cancer. Melatonin may also have an anti-tumor role in the immune system. Studies show melatonin therapy may reduce risk of death in certain cancer types.
5) Weight Loss Aid
Melatonin supplements may help to decrease fat storage. The likely mechanism is increase in release of the hormone leptin. Studies looked at oral melatonin may help with weight reduction in post-menopausal women.
6) Reduce High Blood Pressure
To induce sleep, melatonin acts to decrease blood pressure. Doses of melatonin have been shown to reduce blood pressure in men and women. These changes may be temporary.
7) Reduce Insulin Resistance and Type-II Diabetes
Melatonin regulates the expression of GLUT 4 transporter and may help balance blood sugars related to insulin resistance.
8) Boost Memory
Deep restful sleep helps form new memories. Melatonin may decrease stress and improve sleep for better memory formation.
9) Reverse Tinnitus
Studies show melatonin may be a safe and effective treatment for tinnitus.
10) Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Agent
Melatonin acts as a broad-spectrum antioxidant. It is also an anti-inflammatory agent. Melatonin supplementation was found to suppress exercise induced inflammation.
11) Boost Vision & Eye Health
Melatonin could lower the risk of eye diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
12) Boost Human Growth Hormone
Human growth hormone is naturally released during sleep. In healthy young men, taking melatonin may help increase growth hormone levels.
13) Prevent Heart Disease
Melatonin could be cardio protective.
14) Reverse Infertility and Balance Sex Hormones
Melatonin affects menstruation and menopause in women. It also acts on the testes in men to release testosterone.
15) Longevity and Anti-Ageing
Melatonin could even increase life-span.
The Pineal and Pituitary Gland Endocrine System
When we look at the list above, we can clearly see how influential the pineal gland and melatonin are. The pineal gland acts the master endocrine gland, meaning it signals the other glands, including the pituitary gland, where hormones are usually released from.
Pineal Gland
↓
Hypothalamus
↓
Pituitary Gland
↓
Thyroid Gland / Thymus / Adrenal Gland / Kidneys / Reproductive Glands
If you have any hormone disorder whatsoever, you need to consider how you can get better quality sleep, and also your melatonin levels. Remember that the pineal gland releases melatonin in response to light, so it’s important to sleep in a dark environment and to stop looking at screens in the hours before you go to bed.
Conclusion
The pineal gland is the brain’s master endocrine gland. It directs circadian rhythm via the release of melatonin in response to light and dark cycles. However, melatonin is now known to have benefits across nearly every organ system. Directing the release of every hormone in the body, the pineal gland is in higher control of all organs.
In the last part of this series we’ll explore how to decalcify the third eye.
Further reading:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16648247
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5446506/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20443220
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16207291
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4352910/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14732734
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18853147
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16455366
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21615492
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17266777
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8370132
Now we want to hear from you. Please leave your questions in the comments below.
For more information on Dr. Lin’s clinical protocol that highlights the steps parents can take to prevent dental problems in their children: Click here.







